Curious about how electric bikes work? Look no further! In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of the inner workings of electric bikes. Whether you’re new to the world of electric biking or simply looking to expand your knowledge, we’ve got you covered. From understanding the basics to exploring the tips and tricks to enhance your riding experience, this article aims to equip you with everything you need to know about electric bikes. So, hop on and let’s uncover the secrets behind these fascinating modes of transportation!
Overview
Electric bikes, also known as e-bikes, are becoming increasingly popular for their convenience, efficiency, and eco-friendly nature. These bicycles are equipped with a motor and a battery, which work together to provide assistance to the rider. In this article, we will discuss the basic operation of an electric bike, its components, and the various types of e-bikes available in the market.
Basic Operation
Pedal-assist system
One of the most common types of electric bike systems is the pedal-assist system. As the name suggests, this system provides assistance to the rider when they pedal. When you start pedaling, a sensor detects your pedaling motion and sends a signal to the motor to provide assistance. The level of assistance can usually be adjusted, allowing you to choose how much support you want.
Throttle-based system
Another type of electric bike system is the throttle-based system. With this system, you can control the motor’s assistance with a throttle, similar to how you would accelerate a motorcycle or a scooter. By twisting or pressing the throttle, you can activate the motor and enjoy the added power without having to pedal. This system is especially useful if you need a boost of power, such as when starting from a standstill or climbing a steep hill.
Combination systems
Some electric bikes combine both pedal-assist and throttle-based systems. These combination systems offer the best of both worlds, allowing you to choose between pedaling with assistance or relying solely on the motor. This versatility provides flexibility for different riding situations and preferences.
This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Components
To understand how electric bikes work, it is important to familiarize yourself with the various components that make up these bicycles. Here are the key components found in most electric bikes:
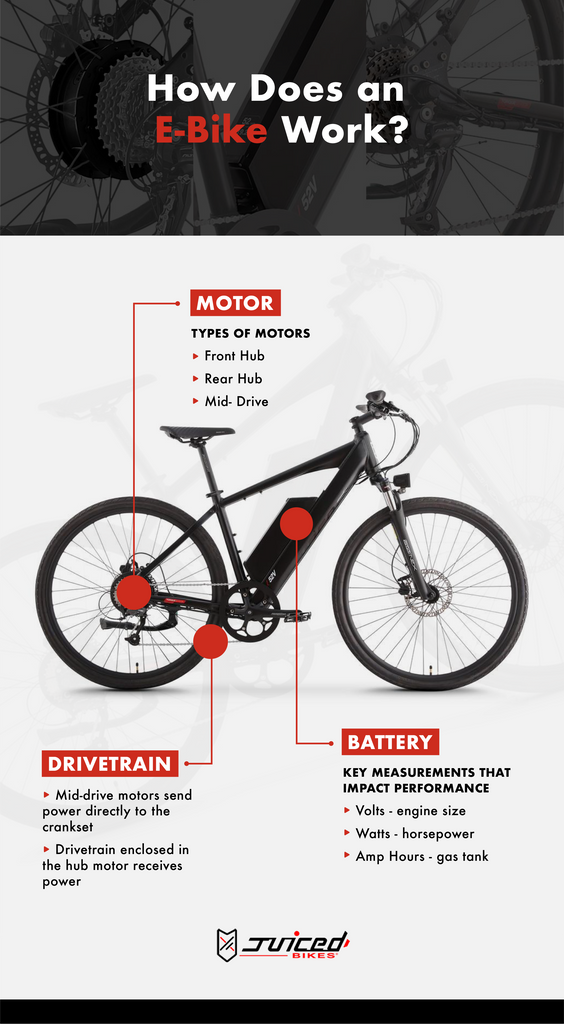
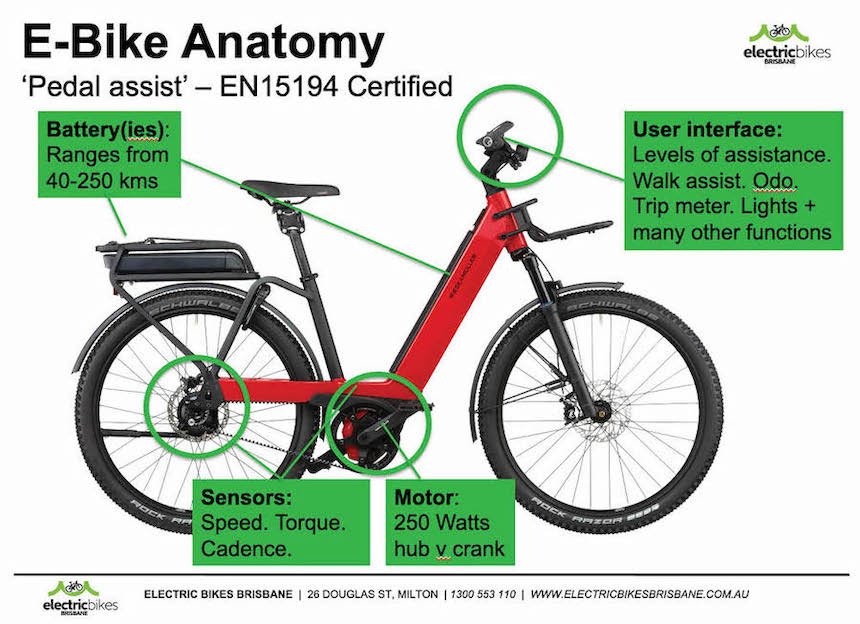
Battery
The battery is the heart of an electric bike. It stores the energy that powers the motor. Most electric bikes use lithium-ion batteries due to their high energy density, durability, and lightweight. The capacity of the battery determines how far you can ride on a single charge.
Motor
The motor is responsible for providing the necessary power to assist you while riding. There are two main types of motors commonly used in electric bikes:
- Hub motors: These motors are integrated into the wheel hub, either in the front or rear wheel. They provide direct drive and are known for their simplicity and low maintenance.
- Mid-drive motors: These motors are mounted in the middle of the bike frame, usually near the bottom bracket. They transfer power to the drivetrain, allowing for better weight distribution and more efficient climbing abilities.
Controller
The controller acts as the brain of the electric bike system. It receives input from the sensors and controls the motor’s power output accordingly. The controller also manages other functions such as battery monitoring, temperature regulation, and safety features.
Sensors
Electric bikes are equipped with various sensors to provide real-time data to the controller. These sensors include:
- Speed sensor: Measures the speed at which you are riding.
- Cadence sensor: Detects how fast you are pedaling.
- Torque sensor: Measures the force applied to the pedals.
- Combined sensor systems: Some electric bikes use a combination of sensors to provide more accurate and responsive assistance.
Display
The display is usually located on the handlebars and provides important information such as speed, distance traveled, battery level, and assistance level. It allows you to monitor your ride and adjust settings if necessary.
Wiring
Electric bikes have a complex wiring system that connects the various components. Proper wiring ensures that all components work together seamlessly and safely.
Types of Electric Bikes
When it comes to electric bikes, there are several different types to choose from, each designed to cater to specific riding needs. Here are some common types of e-bikes:
Class 1 e-bikes
Class 1 e-bikes are equipped with a pedal-assist system that provides assistance only when the rider is pedaling. The motor stops providing assistance once the bike reaches a speed of 20 miles per hour (32 kilometers per hour).
Class 2 e-bikes
Class 2 e-bikes feature a throttle-based system that allows the rider to activate the motor without the need for pedaling. The maximum speed is still limited to 20 miles per hour (32 kilometers per hour).
Class 3 e-bikes
Class 3 e-bikes are similar to Class 1 e-bikes but have a higher top speed. They can provide assistance up to 28 miles per hour (45 kilometers per hour) and are often equipped with additional safety features such as lights and mirrors.
Speed pedelecs
Speed pedelecs are designed for more experienced riders who want the benefits of electric assistance but with higher speeds. These e-bikes can reach speeds of 28 miles per hour (45 kilometers per hour) or more. However, they may be subject to different regulations depending on the jurisdiction.

This image is property of cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net.
Battery
The battery is a crucial component of an electric bike as it determines the range and performance of your ride. Here are some key considerations when it comes to batteries:
Types of batteries
The most common type of battery used in electric bikes is the lithium-ion battery. These batteries are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged many times without losing capacity. Other types of batteries, such as lead-acid and nickel-metal hydride, are less commonly used due to their weight and lower energy density.
Battery capacity
Battery capacity is measured in watt-hours (Wh), and it determines how far you can ride on a single charge. The higher the watt-hour rating, the longer the range. However, it is important to note that other factors such as terrain, rider weight, and assistance level can also affect the range.
Battery management system
A battery management system (BMS) is responsible for monitoring and protecting the battery during charging and discharging. It helps prevent overcharging, overdischarging, and overheating, ensuring the longevity and safety of the battery.
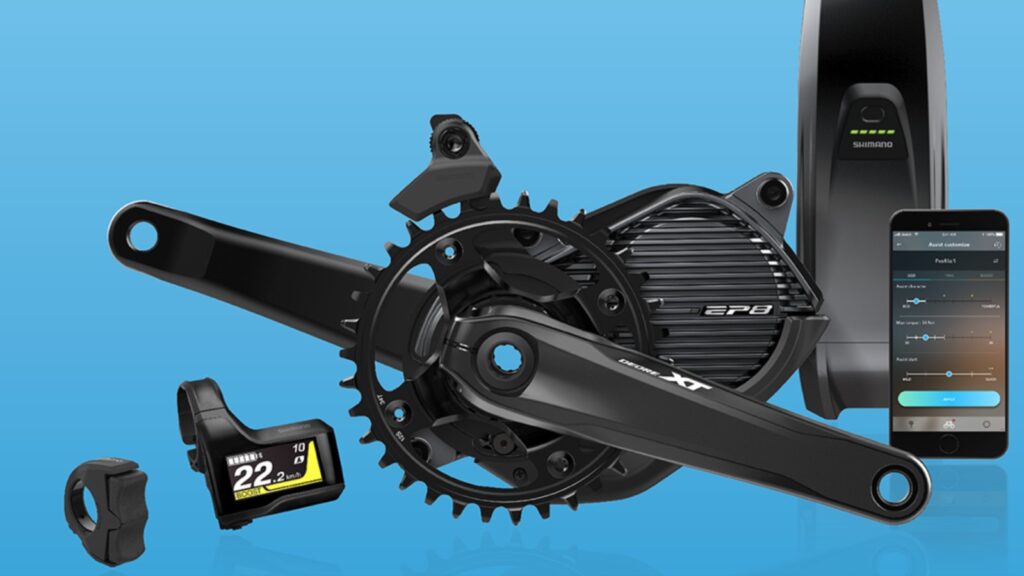
Motor
The motor is what provides the power to assist you while riding. Here are some key factors to consider when it comes to electric bike motors:
Hub motors
Hub motors are integrated into the wheel hub, either the front or rear wheel. They are known for their simplicity, low maintenance, and direct drive. However, they can add weight to the wheels, affecting the overall handling of the bike.
Mid-drive motors
Mid-drive motors are mounted near the bottom bracket of the bike frame. They transfer power to the drivetrain, allowing for better weight distribution and improved climbing abilities. Mid-drive motors are known for their efficiency and responsiveness.
Power output
The power output of an electric bike motor is measured in watts (W). Higher wattage motors generally provide more assistance and are suitable for riders who need extra power or plan to ride in hilly terrain.
Motor control
Motor control refers to how the motor responds to the rider’s input and adjusts the assistance level accordingly. Some motors offer multiple assistance modes, allowing you to choose the level of support that best suits your needs.

This image is property of images2.giant-bicycles.com.
Controller
The controller plays a crucial role in managing the electric bike’s system and ensuring smooth operation. Here are some important aspects of e-bike controllers:
Function
The controller acts as the interface between the sensors, battery, motor, and other components. It receives input from the sensors and adjusts the motor’s power output accordingly. It also performs other functions such as battery monitoring and temperature regulation.
Types of controllers
There are various types of controllers available, ranging from basic models with limited features to advanced controllers with programmable settings. The type of controller used in an electric bike depends on its intended use and budget.
Programming and settings
Some controllers allow you to adjust settings such as assistance level, maximum speed, and even throttle sensitivity. These programmable settings provide customization options, allowing you to fine-tune your electric bike to your preferences.
Sensors
Sensors play a crucial role in providing real-time data to the controller, allowing it to adjust the motor’s assistance accordingly. Here are some commonly used sensors in electric bikes:
Speed sensor
A speed sensor measures the speed at which you are riding. It provides data to the controller, which uses this information to determine the appropriate level of assistance.
Cadence sensor
A cadence sensor detects how fast you are pedaling. It provides feedback to the controller, allowing it to adjust the motor’s assistance based on your pedaling speed.
Torque sensor
A torque sensor measures the force applied to the pedals. It provides precise and responsive assistance by adjusting the motor’s power output based on the rider’s pedaling effort.
Combined sensor systems
Some electric bikes use a combination of sensors to provide more accurate and responsive assistance. These combined sensor systems often include a combination of speed, cadence, and torque sensors.
This image is property of cdn.shopify.com.
Display
The display is an essential part of an electric bike as it provides important information and allows you to control various settings. Here are some key aspects of e-bike displays:
Purpose
The primary purpose of an e-bike display is to provide real-time information about your ride. This includes data such as speed, distance traveled, battery level, and assistance level. The display also allows you to control settings and adjust the bike’s operation if necessary.
Types of displays
There are various types of displays available, ranging from basic LCD screens to full-color TFT displays. The type of display used depends on the e-bike model and its intended use.
Display features
Advanced displays often come with additional features such as integrated navigation, smartphone connectivity, and even fitness tracking. These features enhance the overall riding experience and provide added convenience.
Conclusion
Electric bikes offer a convenient and eco-friendly alternative to traditional bicycles. By understanding the basic operation and components of electric bikes, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right e-bike for your needs. Whether you prefer a pedal-assist system, a throttle-based system, or a combination of both, electric bikes provide a fun and efficient way to navigate your urban or off-road environment. So hop on an electric bike and enjoy the ride!




