If you’ve ever been curious about how electric bike motors work and why they’re crucial for electric bikes, this article is for you. We’ll take a comprehensive look at the heart of electric bikes: the motors. By understanding the different types of motors, their functions, and their impact on e-bike performance, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering behind these innovative vehicles. From hub motors to mid-drive motors, we’ll explore the differences and highlight the market trends that shape the industry. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of electric bike motors and see why they’re essential for an electrifying ride.
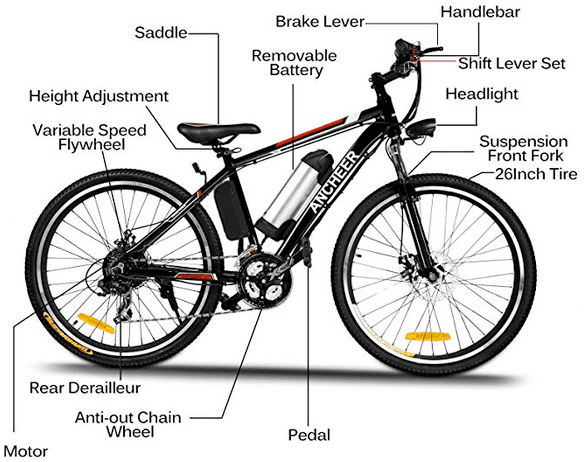
1. Understanding Electric Bike Motors
1.1 How Electric Motors Function
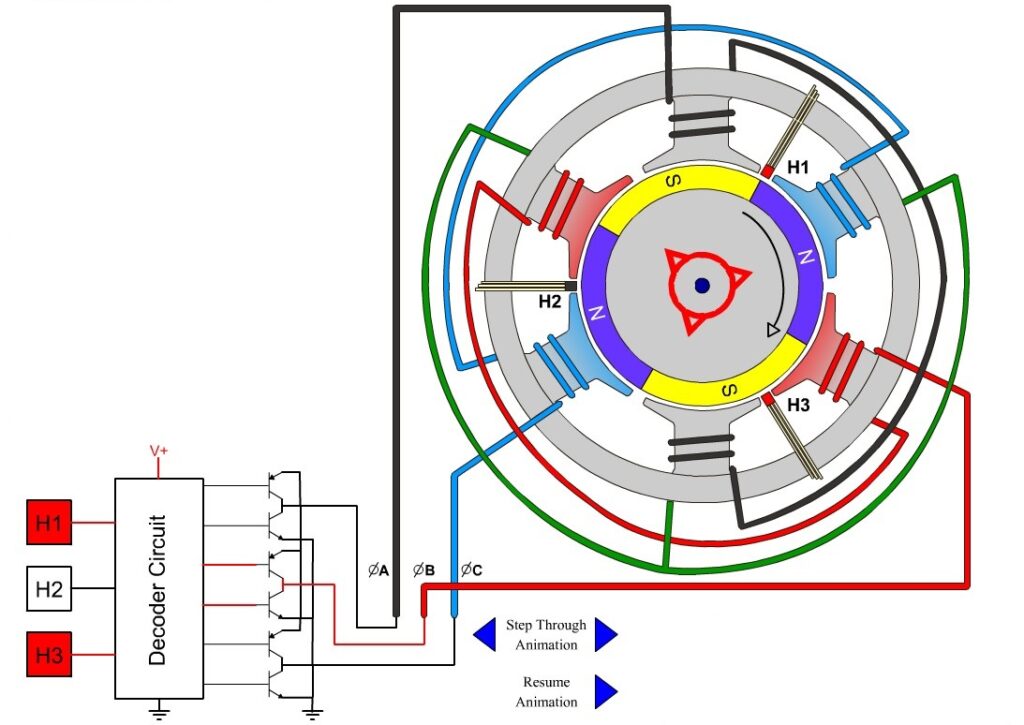
Electric bike motors are the powerhouses that propel you forward on your electric bike adventures. Understanding how these motors function is essential to fully appreciate their capabilities. Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, creating the force necessary to turn the bike’s wheels. They consist of several components, including a stator, rotor, and a set of magnets.
When an electric current flows through the motor’s stator windings, it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the magnets on the rotor, causing it to rotate. The rotating rotor then transfers this motion to the bike’s drivetrain, ultimately powering the wheels and providing the assistance needed during pedaling.
1.2 Importance of Electric Motors in Electric Bikes
Electric motors play a crucial role in the overall performance and functionality of electric bikes. They enable riders to effortlessly conquer challenging terrains, commute long distances without breaking a sweat, and enjoy a more enjoyable and efficient ride.
These motors provide pedal-assist or full-throttle options, allowing riders to choose the level of support they desire. Whether you’re tackling steep inclines, battling strong headwinds, or simply want to ride with ease, the electric motor will significantly enhance your riding experience.
1.3 Factors Affecting Electric Bike Motor Efficiency
Several factors influence the efficiency of electric bike motors. One of the primary factors is the motor’s design and construction, including the quality of the materials used and the precision of its engineering. Higher-quality motors tend to have lower frictional losses and higher energy conversion rates, resulting in greater efficiency.
The weight of the rider and the load on the bike also impact motor efficiency. Lighter loads place less strain on the motor, allowing it to operate more efficiently. Additionally, battery condition and charge level can affect motor performance. A well-maintained and adequately charged battery ensures optimal power delivery to the motor, maximizing its efficiency.
1.4 Market Trends in Electric Bike Motors
The market for electric bike motors is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the growing demand for electric bikes. One notable trend is the shift towards smaller and lighter motors. Manufacturers are developing compact yet powerful motors that take up less space, allowing for sleeker designs and improved handling.
Another significant trend is the integration of smart features into electric bike motors. These features include connectivity capabilities, smartphone apps, and intelligent sensors that optimize motor performance based on riding conditions. Motor manufacturers are also focusing on enhancing motor efficiency by utilizing advanced control algorithms and regenerative braking systems.
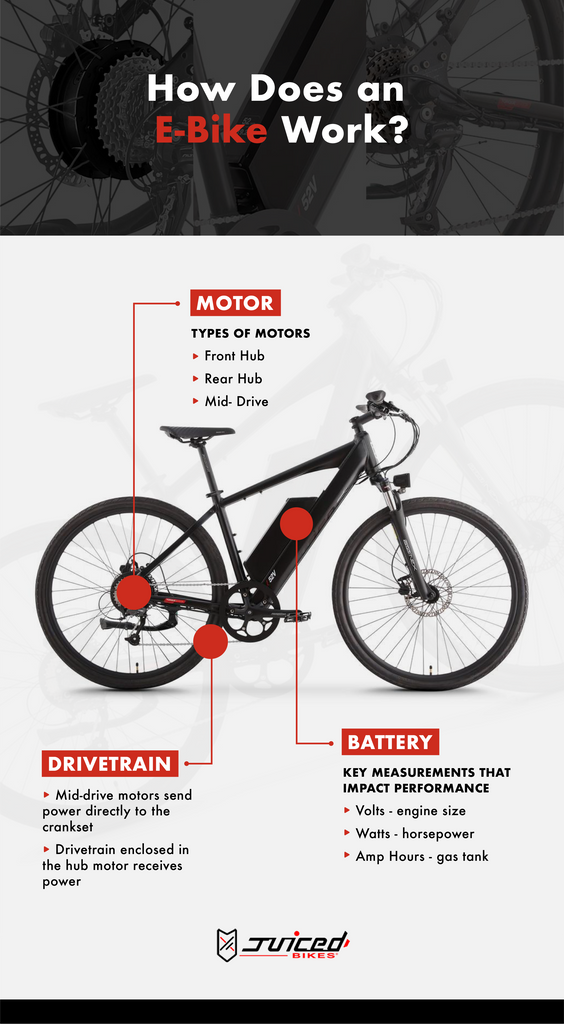
2. Types of Electric Bike Motors
Electric bikes offer various motor options to cater to different riding styles and preferences. Let’s explore the four main types of electric bike motors:
2.1 Hub Motors
Hub motors are the most common type of electric bike motors. As the name suggests, they are integrated into the hub of one or both wheels. Hub motors can be further categorized into two subtypes: front hub motors and rear hub motors.
Front hub motors provide assistance by directly driving the front wheel. They are relatively simple in design and installation, making them a popular choice for e-bike conversions. Rear hub motors, on the other hand, drive the rear wheel and offer better traction, especially on uphill climbs.
2.2 Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors, also known as crank motors or central motors, are positioned at the bike’s bottom bracket, where the pedals are located. These motors transfer power directly to the bike’s drivetrain, providing a more natural and balanced riding experience. Mid-drive motors are highly efficient and offer better weight distribution, resulting in improved handling and maneuverability.
2.3 Direct Drive Motors
Direct drive motors, also referred to as gearless motors, offer a smooth and quiet ride. They don’t have any gears and rely on electromagnetic force to generate motion. Direct drive motors are known for their durability and longevity. They provide robust torque, making them ideal for high-performance electric bikes.
2.4 Geared Motors
Geared motors combine the benefits of a direct drive motor with the mechanical advantage of gears. By incorporating a planetary gear set, geared motors can achieve higher torque without sacrificing efficiency. These motors are popular for off-road and mountain bike applications, where enhanced torque can conquer challenging terrains.
3. Hub Motors
3.1 Overview of Hub Motors
Hub motors are the workhorses of the electric bike world, offering simplicity and reliability. They are self-contained units that require minimal maintenance, making them a popular choice among electric bike enthusiasts. Hub motors come in various sizes and power levels to cater to different riding preferences and terrain types.
One of the key advantages of hub motors is their ease of installation. With a few basic tools, you can convert a regular bike into an electric bike by simply replacing the existing front or rear wheel with a hub motor wheel. This accessibility has contributed to the widespread popularity of hub motor-equipped electric bikes.
3.2 Pros and Cons of Hub Motors
Hub motors offer several advantages that make them attractive to electric bike riders. Firstly, they provide a smooth and quiet ride. With no gears to shift and minimal moving parts, hub motors deliver a virtually noiseless experience. This makes them particularly appealing to riders who value a peaceful and enjoyable journey.
Hub motors also offer excellent torque output, allowing for quick acceleration and effortless climbing. With power directly applied to the wheels, riders can conquer steep hills and challenging terrains without breaking a sweat. Additionally, hub motors require little to no maintenance, minimizing the hassle and cost associated with upkeep.
While hub motors have many benefits, they also have a few limitations. One common drawback is their weight distribution. With the motor located at the wheel, the bike’s weight can become unbalanced, affecting handling and maneuverability. Hub motors also don’t take advantage of the bike’s gears, potentially limiting efficiency and performance in certain situations.
3.3 Types and Variations of Hub Motors
Hub motors come in various types and configurations to suit different riding needs. These variations include different power outputs, wheel sizes, and compatibility with different types of e-bikes.
Low-power hub motors are typically found in compact and lightweight electric bikes designed for urban commuting or recreational riding. These motors offer efficient assistance at lower speeds and are suitable for relatively flat terrains.
High-power hub motors, on the other hand, are designed for off-road and mountain biking applications. These motors deliver substantial torque, enabling riders to tackle steep inclines and challenging trails with ease.
Hub motors are also available for different wheel sizes, including 26-inch, 27.5-inch, and 700c. This allows riders to match the motor to the specific wheel size of their bike, ensuring proper fitment and optimal performance.
4. Mid-Drive Motors
4.1 Introduction to Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors are gaining popularity among electric bike enthusiasts due to their unique advantages. Unlike hub motors, which drive the wheels directly, mid-drive motors are situated at the bike’s bottom bracket, where the cranks and pedals connect. This positioning allows the mid-drive motor to work in harmony with the bike’s gears, resulting in a more efficient and versatile power delivery system.
By leveraging the bike’s existing gear ratios, mid-drive motors can provide assistance across a wider range of speeds and terrains. They ensure that the motor operates at its optimal RPM, maximizing efficiency and extending battery range. The ability to utilize the bike’s gears also allows mid-drive motors to maintain a higher average speed while conserving energy.
4.2 Advantages of Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors offer several advantages that make them a compelling option for electric bike riders. Firstly, they provide a more natural riding experience. By driving the bike’s drivetrain directly, mid-drive motors distribute power evenly between the front and rear wheels. This balanced power delivery enhances traction and control, particularly in challenging off-road or steep uphill scenarios.
Another significant advantage of mid-drive motors is their superior climbing ability. By leveraging the bike’s gears, these motors can deliver maximum torque precisely when needed, allowing riders to conquer the steepest hills effortlessly. The ability to climb with ease expands the possibilities for adventure, making mid-drive motor-equipped bikes ideal for off-road exploration.
4.3 Considerations for choosing Mid-Drive Motors
When considering a mid-drive motor for your electric bike, there are several important factors to take into account. One key consideration is the motor’s power output. Higher-power mid-drive motors provide more torque, allowing for better climbing ability and improved overall performance. However, it’s essential to ensure that the motor is matched with a compatible battery that can deliver the necessary power.
The motor’s weight is another crucial consideration. Mid-drive motors add weight to the bike’s central area, which can affect handling and maneuverability. Opting for a lightweight mid-drive motor is advisable, particularly if you prioritize nimble and agile riding characteristics.
Lastly, it’s important to assess the noise and vibration levels of the mid-drive motor. Some motors may produce noticeable noise or vibration, which can impact ride comfort. Checking customer reviews and conducting research on specific motor models can help in selecting a quieter and smoother mid-drive motor.
5. Direct Drive Motors
5.1 Understanding Direct Drive Motors
Direct drive motors, also known as gearless motors, operate on a different principle compared to hub motors and mid-drive motors. These motors rely solely on the interaction between electromagnetic fields and magnets to generate rotational force. Unlike other motor types, direct drive motors don’t have any internal gears.
Direct drive motors are known for their simplicity and durability. With fewer moving parts, there are fewer components that can wear out or require maintenance. They provide a smooth and silent ride, making them a popular choice for electric bike riders who prioritize a quiet and peaceful cycling experience.
5.2 Benefits and Limitations of Direct Drive Motors
Direct drive motors offer several unique benefits that set them apart from other motor types. Firstly, they provide high torque output, making them ideal for riders seeking robust and reliable power. This torque allows electric bikes equipped with direct drive motors to excel in challenging terrains, effortlessly tackling steep hills and rocky trails.
Another advantage of direct drive motors is their ability to deliver regenerative braking. When the rider applies the brakes, the motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy of the moving bike into electrical energy and storing it in the battery. This regenerative braking system helps increase overall energy efficiency and extend battery range.
However, direct drive motors also have limitations to consider. One notable drawback is their weight. Direct drive motors are typically heavier than other motor types due to the absence of internal gears. This extra weight can impact the bike’s overall weight and handling characteristics, requiring riders to exert more effort during pedaling when the motor is not engaged.
Additionally, direct drive motors may not provide the same level of efficiency at lower speeds compared to other motor types. The absence of gears limits the motor’s ability to optimize power delivery for various riding conditions, potentially affecting energy consumption.
5.3 Applications of Direct Drive Motors
Direct drive motors find their niche in specific electric bike applications. They are particularly well-suited for high-performance electric bikes and e-bikes designed for off-road adventures. Due to their high torque output, direct drive motors provide the necessary power to conquer rugged terrains, offering a thrilling and capable ride.
For recreational riders or those looking to enjoy a peaceful and leisurely cycling experience, the smooth and silent operation of direct drive motors can be a major draw. These motors offer a serene ride with minimal noise and vibration, enhancing the overall enjoyment of the journey.
6. Geared Motors
6.1 Exploring Geared Motors
Geared motors blend the advantages of direct drive motors with the mechanical efficiency of gears. These motors incorporate a planetary gear set that allows for increased torque output and improved climbing ability without sacrificing overall efficiency.
The planetary gear set consists of multiple gears working together in a compact arrangement. They allow the motor to deliver higher torque while maintaining lower RPM, optimizing power delivery and conserving energy. The use of gears also enables riders to take advantage of the bike’s gears, ensuring efficient power transfer across a wide range of riding speeds and terrains.
6.2 Advantages of Geared Motors
Geared motors offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for electric bike riders. Firstly, they provide excellent torque output, allowing for enhanced climbing ability and improved acceleration. This increased torque is particularly beneficial for riders who frequently encounter steep inclines or need extra power for off-road adventures.
Another advantage of geared motors is their compact size and weight. Compared to other motor types, geared motors are generally smaller and lighter, contributing to improved handling and maneuverability. The reduced weight also helps increase overall energy efficiency and battery range.
Additionally, geared motors offer improved power delivery across different riding speeds. By utilizing the bike’s gears, the motor can operate within its optimal RPM range, delivering efficient and responsive support. This adaptability ensures a smooth and enjoyable riding experience across various terrains and riding conditions.
6.3 Types and Specifications of Geared Motors
There are various types and specifications of geared motors available for electric bikes. These variations include different power outputs, gear ratios, and compatibility with different e-bike configurations.
Higher-power geared motors are often preferred by riders who prioritize torque and acceleration. These motors deliver robust performance, making them suitable for off-road, mountain biking, or carrying heavier loads. Lower-power geared motors, on the other hand, are commonly used in urban commuting or recreational riding applications, where a balanced blend of assist and efficiency is desired.
The gear ratio of a geared motor determines the trade-off between torque and speed. Lower gear ratios result in higher torque output, ideal for climbing or starting from a standstill. Higher gear ratios, on the other hand, prioritize speed and are better suited for flat or rolling terrains.
When choosing a geared motor, it’s important to ensure it is compatible with your specific e-bike configuration. Consider factors such as frame compatibility, torque sensor integration, and overall system efficiency to find the best match for your riding needs.
7. Motor Performance
7.1 Power Output and Torque
When evaluating electric bike motors, considering their power output and torque capabilities is crucial. Power output is typically measured in watts (W) and refers to the motor’s ability to deliver a certain amount of energy per unit of time. Higher power output allows for greater acceleration and higher top speeds.
Torque, on the other hand, measures the rotational force or twisting power produced by the motor. It determines the motor’s ability to perform tasks such as climbing steep hills or accelerating from a stop. Higher torque allows for easier hill climbing and improved overall performance, particularly in challenging terrains.
Both power output and torque should be taken into account when choosing an electric bike motor. The optimal balance depends on factors such as riding preferences, terrain types, and the weight being carried.
7.2 Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Efficiency is a vital aspect of electric bike motors, as it directly affects battery range and overall energy consumption. Motor efficiency refers to how well the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency means less energy is lost as heat, resulting in longer battery life and improved range.
Efficiency can be influenced by various factors, including motor design, quality of materials, and overall system integration. Higher-quality motors tend to have better efficiency, as they are engineered with precision and utilize advanced control algorithms. Additionally, factors such as the weight of the bike and rider, terrain conditions, and riding style can impact motor efficiency.
When evaluating motor efficiency, riders should also consider the impact of auxiliary components such as motor controllers and battery management systems. These components play a significant role in determining overall system efficiency and should be matched carefully with the motor to achieve optimal performance.
7.3 Noise and Vibration
Noise and vibration levels can significantly impact the overall riding experience. Electric bike motors that generate excessive noise or vibrations can be distracting and uncomfortable for riders. Therefore, considering the noise and vibration characteristics of a motor is important when selecting the right one for your electric bike.
Direct drive motors and mid-drive motors tend to be quieter compared to hub motors. Motors with high-quality construction, precision engineering, and advanced noise reduction technologies also tend to produce less noise and vibrations.
Rider comfort and preference should guide the decision-making process. Testing or researching the noise and vibration levels of specific motor models can help ensure a smoother, quieter, and more enjoyable ride.
7.4 Understanding Motor Controllers
Motor controllers play a critical role in managing the performance and functions of electric bike motors. These electronic devices regulate the electrical current supplied to the motor, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Motor controllers also enable features such as variable speed control, pedal-assist modes, and regenerative braking.
The quality and capabilities of the motor controller can significantly impact the overall motor performance. Higher-quality controllers offer advanced features and precise control algorithms, resulting in smoother power delivery, enhanced efficiency, and improved riding experience.
When evaluating an electric bike motor, it’s essential to consider the accompanying motor controller. Compatibility between the motor and controller is crucial to achieve optimal performance and ensure smooth integration with other system components.
8. Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electric Bike Motor
Selecting the right electric bike motor involves considering various factors that align with your specific riding needs and preferences. Here are some key factors to consider:
8.1 Intended Use and Terrain
Consider the intended use of your electric bike and the types of terrain you will encounter. If you plan to ride off-road trails or tackle steep hills, a motor with high torque capabilities, such as a mid-drive motor or a geared motor, would be suitable. For urban commuting or leisurely rides on flat terrain, a hub motor or a lower-power mid-drive motor may suffice.
8.2 Battery Compatibility
Ensure that the chosen motor is compatible with the battery system of your electric bike. Consider factors such as voltage, capacity, and type of battery. The motor and battery should work seamlessly together to provide optimal power delivery and performance.
8.3 Motor Power and Torque
Evaluate the power output and torque capabilities of the motor. Higher power output and torque are advantageous for riders who frequently encounter challenging terrains or require extra assistance. Balancing power and torque with battery range and overall system efficiency is important to meet your riding requirements.
8.4 Noise and Vibration
Consider your preference for noise and vibration levels when selecting an electric bike motor. Quieter motors, such as mid-drive motors or direct drive motors, may be preferable for riders seeking a peaceful and comfortable riding experience.
8.5 Cost and Maintenance
Factor in the cost of the motor and ongoing maintenance requirements. Hub motors generally require less maintenance compared to mid-drive motors or direct drive motors. Consider the long-term costs associated with maintenance, repairs, and potential upgrades to make an informed decision.
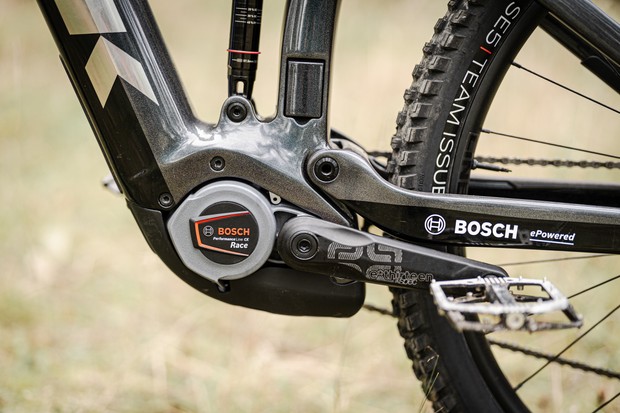

9. Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Electric Bike Motors
9.1 Regular Maintenance Practices
Performing regular maintenance on your electric bike motor is essential to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. Some recommended maintenance practices include:
- Keeping the motor clean and free from debris or obstructions.
- Checking and tightening any loose bolts or connections.
- Regularly inspecting the motor’s wiring and cables for any signs of wear or damage.
- Lubricating moving parts, such as the motor bearings, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Following the recommended battery maintenance practices to ensure a healthy and efficient power supply to the motor.
9.2 Troubleshooting Common Motor Issues
Electric bike motors may occasionally encounter issues that affect their performance. Some common motor issues and troubleshooting tips include:
- Motor not turning on: Check the battery charge, connections, and fuse. Ensure that the motor controller is functioning correctly.
- Low power output: Ensure that the motor is receiving adequate voltage from the battery. Check for any loose or damaged connections.
- Unusual noise or vibration: Inspect the motor for any loose or damaged components. Check the alignment of gears or internal mechanisms.
- Overheating: Ensure proper ventilation and cooling for the motor. Check for any obstructions or excessive load on the motor.
In case of persistent issues or concerns, consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional assistance for diagnosis and repairs.
9.3 Extending Motor Lifespan
Taking steps to extend the lifespan of your electric bike motor can help maximize your investment. Some strategies to consider include:
- Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule.
- Avoiding excessive weight or load on the motor.
- Riding with a proper gear ratio to prevent unnecessary strain on the motor.
- Storing the electric bike in a dry and protected environment to prevent corrosion or damage.
- Adhering to safe riding practices and avoiding extreme operating conditions.
By implementing these practices, you can ensure that your electric bike motor remains in excellent condition, delivering reliable performance for years to come.
10. Conclusion
Electric bike motors are the heart and soul of electric bikes, providing the necessary power and assistance to enhance your riding experience. Understanding the different motor types, their advantages, and their applications is crucial when choosing the right motor for your specific needs. Factors such as power output, torque capabilities, efficiency, and maintenance requirements should be carefully considered to select the ideal motor for your electric bike adventures.
Whether you opt for a hub motor for its simplicity, a mid-drive motor for its efficiency, a direct drive motor for its durability, or a geared motor for its torque, you can rest assured that your electric bike motor will open up new possibilities and make every ride a joyous experience. So, hop on your electric bike, let the motor propel you forward, and embrace the freedom and excitement that electric bike motors bring to your two-wheeled adventures.