If you’re a cycling enthusiast looking to explore the world of electric bikes, understanding the different types of motors is crucial. In this article, we will delve into the heart of electric bikes and provide you with a comprehensive introduction to electric bike motors. You’ll learn about the functions of these motors, why they are essential for e-bike performance, and the key differences between the various motor types. Through this guide, you’ll gain insights into market trends and identify keywords like “electric bike motor efficiency,” “hub motors,” “mid-drive motors,” and “motor performance” that will help you make an informed decision when choosing an electric bike with the right motor for your needs. Let’s get started on this exciting journey of exploring electric bike motor types!
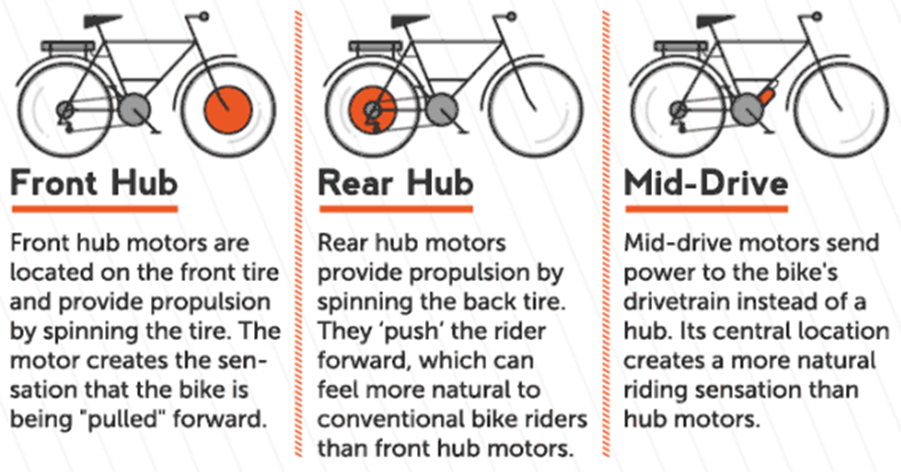
1. Hub Motors
Hub motors are a type of electric bike motor that is built into the hub of the wheel. They come in two main varieties: direct drive hub motors and geared hub motors. Let’s take a closer look at each type.
1.1 Direct Drive Hub Motors
Direct drive hub motors utilize a system where the magnets are stationary, and the wheel is turned by electromagnetic forces. These types of motors are known for their simplicity and durability. They offer a smooth and quiet ride, making them popular among electric bike enthusiasts. Direct drive hub motors also have regenerative braking capabilities, which can help extend the battery life of an electric bike.
1.2 Geared Hub Motors
On the other hand, geared hub motors use gears inside the motor to increase torque and decrease the rotational speed. This allows for better hill climbing ability and increased efficiency. Geared hub motors are generally smaller, lighter, and more efficient than their direct drive counterparts. However, they may produce more noise and vibration due to the presence of gears.
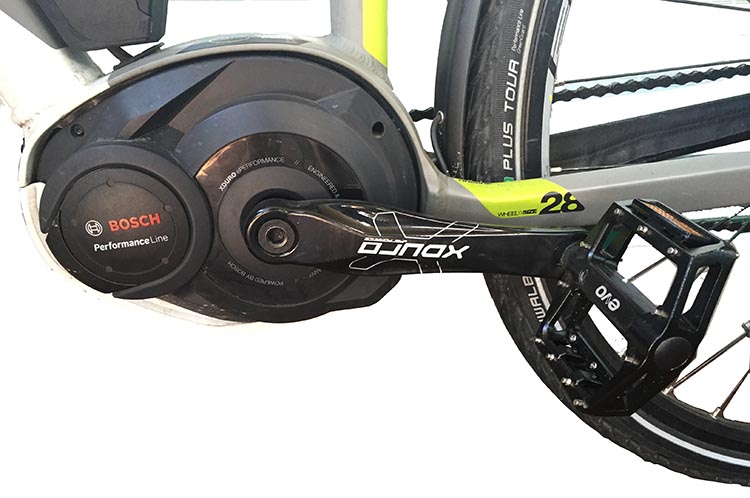
2. Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors, also known as crank drive motors, are mounted in the middle of the bike frame, near the pedals. These motors transfer power to the drivetrain through the chain or belt, allowing for a more natural riding experience. Let’s delve into the definition, functionality, advantages, and disadvantages of mid-drive motors.
2.1 Definition and Functionality
Mid-drive motors work by using the bike’s existing gears to multiply the power produced by the motor. By leveraging the bike’s gearing system, mid-drive motors can provide higher torque and efficiency compared to hub motors. The location of the motor near the drivetrain also ensures better weight distribution and handling.
2.2 Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the main advantages of mid-drive motors is their ability to take advantage of the bike’s existing gears, resulting in better hill climbing performance and improved efficiency. These motors also offer a more balanced weight distribution, allowing for better handling and stability. However, mid-drive motors tend to be more complex and can be noisier compared to hub motors. They also require more maintenance, as they interact directly with the bike’s drivetrain components.
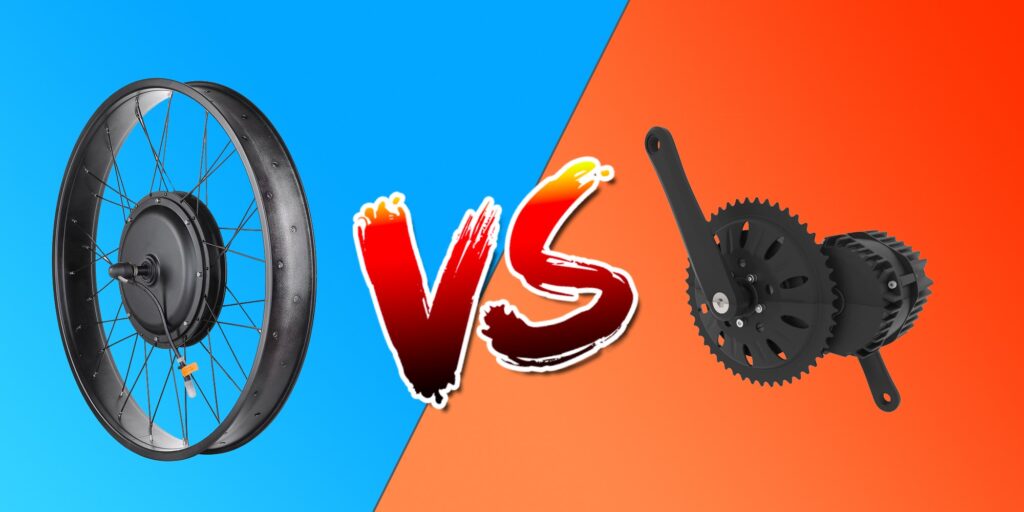

3. Brushless vs. Brushed Motors
In the world of electric bike motors, there are two main types of motors: brushed motors and brushless motors. Let’s explore the differences between these two types.
3.1 Brushed Motors
Brushed motors utilize brushes and a commutator to transfer electricity to the motor’s electromagnets. These motors have been around for a long time and are known for their simplicity and low cost. However, they tend to be less efficient and have a shorter lifespan compared to brushless motors. Brushed motors also produce more heat and require regular maintenance, as the brushes need to be replaced periodically.
3.2 Brushless Motors
Brushless motors, as the name suggests, eliminate the need for brushes by using a more complex internal structure. Instead of brushes, they rely on electronic commutation to control the flow of electricity to the motor’s coils. Brushless motors offer several advantages over brushed motors, including higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and reduced maintenance requirements. They are also quieter and produce less heat during operation, resulting in improved overall performance.
3.3 Pros and Cons
When comparing brushless and brushed motors, it becomes evident that brushless motors are the superior option for electric bikes. They provide better efficiency, durability, and performance, making them the preferred choice for most electric bike manufacturers. Brushed motors, while cheaper, cannot compete with the advantages offered by brushless motors in terms of longevity, maintenance, and overall performance.
4. Power and Torque
Power and torque are crucial considerations when evaluating electric bike motors. Let’s explore how these two measurements affect electric bike performance.
4.1 Power Measurement
When it comes to electric bike motors, power is usually measured in watts. The power rating of a motor determines how much electrical energy it can convert into mechanical energy, which translates into the speed and acceleration of the bike. Generally, higher power motors provide faster acceleration and higher top speeds, but they may also drain the battery more quickly.
4.2 Torque Measurement
Torque, on the other hand, is a measure of the rotational force produced by the motor. It determines the bike’s ability to climb hills and handle uneven terrain. Torque is usually measured in Newton meters (Nm). Higher torque motors excel in hill climbing scenarios, allowing riders to tackle steep inclines with ease.
4.3 Influence on Electric Bike Performance
The balance between power and torque is crucial for achieving optimal electric bike performance. While high power motors can provide fast acceleration, it’s the torque that ultimately determines the bike’s ability to conquer challenging terrains. Finding the right balance between power and torque ensures a smooth and enjoyable riding experience.
5. Efficiency and Battery Life
Efficiency and battery life are essential factors to consider when choosing an electric bike motor. Let’s dive into how the type of motor affects these aspects.
5.1 Motor Efficiency
Motor efficiency refers to how effectively a motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Brushless motors are generally more efficient than brushed motors due to their improved design and electronic commutation. Direct drive hub motors also tend to be more efficient than geared hub motors since there are no gears or associated friction losses.
5.2 Battery Life Impact
The efficiency of the motor directly impacts the battery life of an electric bike. More efficient motors require less energy from the battery to perform the same tasks, allowing for longer rides and increased range. A higher efficiency motor also reduces heat generation, which can further extend the lifespan of the battery.
5.3 Factors Affecting Efficiency and Battery Life
Several factors can affect the efficiency and battery life of an electric bike. These include the motor type, rider weight, terrain, riding style, and battery capacity. It is important to consider all these factors when choosing an electric bike motor to ensure optimal efficiency and battery performance.
6. Noise and Vibration
Noise and vibration can significantly impact rider comfort, especially during long rides. Let’s compare the noise and vibration levels of different motor types.
6.1 Noise Comparison
Hub motors, whether direct drive or geared, are known for their quiet operation. The absence of gears in direct drive hub motors eliminates the potential noise caused by gear meshing. Geared hub motors may produce some level of noise due to the presence of gears. Mid-drive motors, on the other hand, can be noisier compared to hub motors since they interact directly with the drivetrain components.
6.2 Vibration Comparison
Similar to noise levels, hub motors generally produce less vibration compared to mid-drive motors. The smooth and direct power delivery of hub motors results in a more comfortable riding experience. Mid-drive motors, on the other hand, can transmit some level of vibration to the pedals and bike frame, especially at higher speeds or when climbing steep hills.
6.3 Impact on Rider Comfort
Reduced noise and vibration levels contribute to a more enjoyable and comfortable ride. Hub motors, with their quiet and smooth operation, offer a more pleasant riding experience, especially for casual riders or those looking for a relaxing commute. However, some riders may prefer the additional feedback provided by mid-drive motors, as it can enhance the overall riding experience.
7. Hill Climbing Performance
Hill climbing ability is a significant consideration when choosing an electric bike motor. Let’s explore how different motor types perform in challenging uphill conditions.
7.1 Hub Motors vs. Mid-Drive Motors
When it comes to hill climbing, mid-drive motors are generally considered superior to hub motors. The location of mid-drive motors near the bike’s drivetrain allows them to take advantage of the bike’s gears, providing increased torque and better hill climbing ability. Hub motors, while capable of climbing hills, may struggle in steeper or more challenging terrains.
7.2 Power and Torque Considerations
Both power and torque play important roles in hill climbing performance. Higher torque motors are better equipped to handle uphill climbs, as they can provide the necessary rotational force to conquer steep gradients. However, it’s essential to find the right balance between power and torque to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
7.3 Real-World Performance
In real-world scenarios, the performance of an electric bike motor is influenced by various factors, including rider weight, bike weight, terrain, and riding style. While mid-drive motors generally excel in hill climbing, modern hub motors have significantly improved their performance in recent years. Riders should consider their specific needs and riding conditions when choosing between hub motors and mid-drive motors for optimal hill climbing performance.
8. Weight Distribution
The distribution of weight on an electric bike can affect its handling and stability. Let’s examine how different motor types impact weight distribution.
8.1 Hub Motors
Hub motors are typically located in the center of the wheel, which results in a more rear-heavy weight distribution. This can affect the bike’s handling, making it feel slightly sluggish or less responsive compared to bikes with mid-drive motors. However, this rear-heavy distribution can also provide better traction and stability, especially when riding on slippery or loose surfaces.
8.2 Mid-Drive Motors
Mid-drive motors, being located near the bike’s bottom bracket, provide a more balanced weight distribution. This balanced distribution improves overall handling and maneuverability, allowing for better control and responsiveness. The weight of the motor being centralized also contributes to better stability and balance.
8.3 Handling and Stability Effects
The weight distribution of an electric bike can significantly impact its handling and stability. Riders who prioritize nimble and responsive handling may prefer mid-drive motors for their balanced weight distribution. On the other hand, riders who prioritize stability and traction may lean towards hub motors, particularly for off-road or challenging terrains.

9. Price and Market Trends
Cost and market trends are important considerations for many electric bike buyers. Let’s explore the cost differences between motor types and the current market trends.
9.1 Cost Difference Between Motor Types
The cost of electric bike motors can vary depending on the type and quality of the motor. Generally, hub motors are less expensive than mid-drive motors due to their simpler design and fewer components. Mid-drive motors tend to be more sophisticated and require additional drivetrain components, which can drive up the overall cost of the bike.
9.2 Availability and Demand
The demand for electric bikes has been steadily increasing over the years, leading to a wider availability of both hub motors and mid-drive motors. As the technology improves, more manufacturers are incorporating electric bike motors into their product lineup, providing consumers with a greater variety of choices.
9.3 Emerging Technologies
The electric bike industry is continually evolving, and new technologies are emerging to improve motor performance and efficiency. Some emerging technologies include torque sensors, which allow for more precise power delivery based on rider input, and integrated motor and battery systems, which streamline the design and offer improved performance.
10. Conclusion
Choosing the right motor for your electric bike is crucial to ensure optimal performance and satisfaction. When considering different motor types, it’s essential to evaluate factors such as power, torque, efficiency, weight distribution, noise, and vibration. Additionally, considering personal preferences, riding style, terrain, and budget will help you make an informed decision.
10.1 Key Considerations for Choosing the Right Motor
- Understand your riding needs and terrain requirements.
- Consider the trade-offs between power, torque, efficiency, noise, and vibration.
- Evaluate the weight distribution and its impact on handling and stability.
- Assess the cost differences between different motor types and consider your budget.
- Stay informed about emerging technologies and market trends.
10.2 Future Development Prospects
As technology advances and the demand for electric bikes continues to grow, we can expect further advancements in motor design and performance. Continued improvements in efficiency, integration, and battery technology will likely shape the future of electric bike motors. It’s an exciting time to be part of the electric bike revolution, with endless possibilities for future development and innovation.




